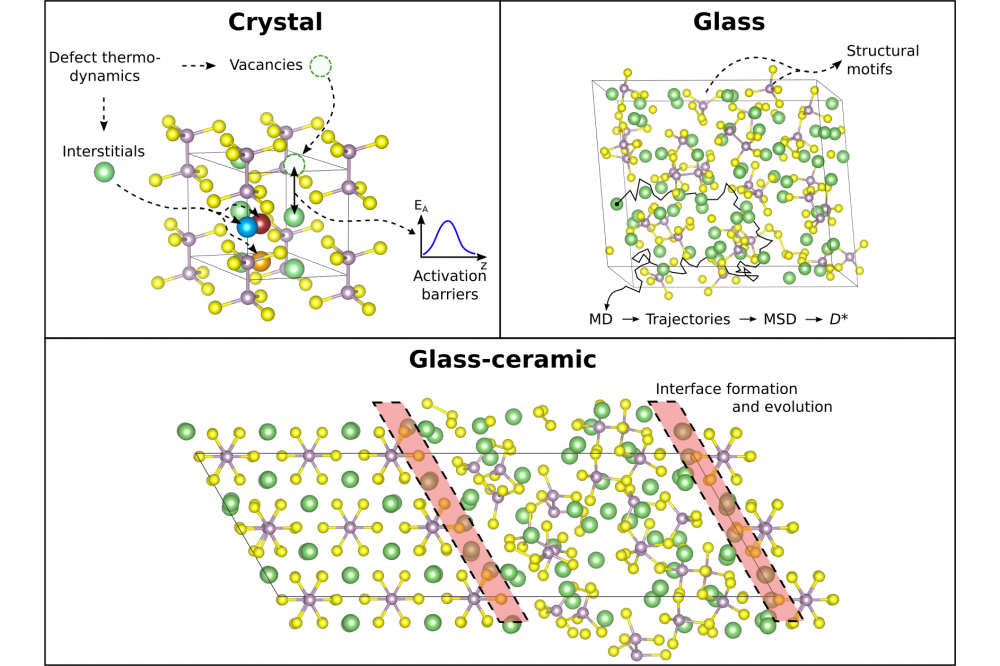
Figure 1: Sketch of our methodology for analyzing lithium thiophosphate glass ceramics. First (top, left) defect thermodynamics of point defects are investigated in crystalline structures. Where applicable, activation barriers can be calculated via nudged elastic band (NEB) calculations. Next, amorphous glass structures are generated with a melt quenching protocol using ab-initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) and the underlying structural motifs can be analyzed (top, right). Structures can be idealized if information from experiments are provided. Furthermore, transport properties like tracer diffusion coefficients (D*) are accessible via AIMD simulations at different temperatures. In the last step (bottom), interfaces can be assembled and their structure, interphases and evolution can be investigated. Defect thermodynamics can be helpful to evaluate the interface stability.