Application of a Hybrid Filtered Eulerian Stochastic Field/Flamelet Progress Variable Method on a Non-Premixed Oxy-Flame Cases Using OpenFOAM Code
Einleitung
Nowadays the fuels combustion still sustain most of the energy needs and its productions. Different studies have been inducted to understand and conceive this process especially when turbulence is interacted with combustion where many challenges needs to be deeply investigated. The fact of supposing to such challenges experimentally may be very demanding and expensive. Thereby, numerical methods have been introduced and developed to treat this phenomena and detect different turbulence-combustion interaction properties.
Methoden
The Probability Density Function (PDF) methods have been evaluated within many researches dealing with different cases and proved to be promising methods. However, some turbulencecombustion properties are still numerically challenging to be appropriately reproduced. Thereby a novel numerical method based on PDF concept was suggested, evaluated and validated by comparing simulations outcome from previous projects with existing reference data (Experimental measurements). This novel approach consists on a combination between Transported Joint Probability Density Function (TPDF) pursuing the Eulerian Stochastic Field Method (ESF) and a tabulated chemical tool following the Flamelet Progress Variable (FPV). The reader is referred to Mahmoud et al. in [1, 2] for more details. Regarding the evaluation and validation phase of the solver, both RANS and LES frameworks have been applied to investigate the test case of piloted-jet Sandia Flame-D (see [3]) and the challenging case of the Oxy-fuel series {B3,A1,A3} (see[4]) with different stages. The grid meshes of the considered configurations were relative fine and different stochastic fields have been applied which explain the need to perform the different calculations on high performance computer systems on the Lichtenberg cluster.
Ergebnisse
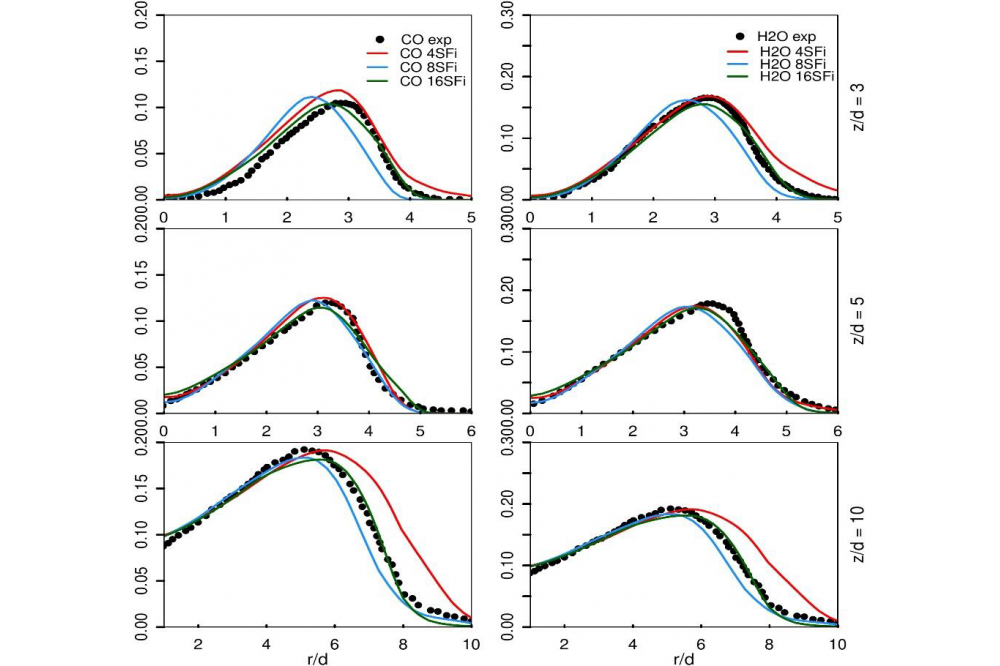
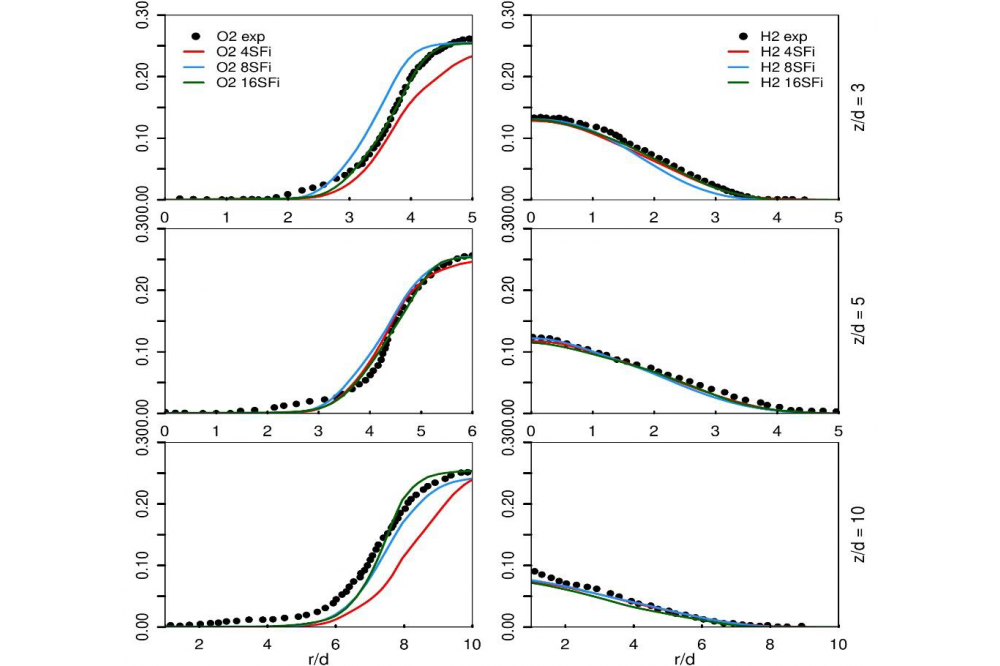
The numerical results, obtained by applying the hybrid ESF/FPV method on piloted jet flame Sandia-D and Oxy-fuel series {A1, A3, B3} in the RANS framework, showed a very good agreement with available experimental data and better prediction of combustion properties related to CO and H2O species and Temperature field, once compared to the usual existing presumed PDF method that was applied in order to analyse different numerical methods performance. This outcome is reported in Mahmoud et al in [1]. In the LES Framework, the implemented solver was also successfully validated by using coarse grids and applying 4 and 8 stochastic fields during calculation for both cases, and more additional test with 16 Stochastic fields for the Oxy-fuel flame B3 (see Figure 1 ). The reader is referred to Mahmoud et al in [2] for more details.
Diskussion
The findings of the application of the novel ESF/FPV method in both RANS and LES frameworks demonstrated the good performance of the numerical tool in the prediction of turbulencecombustion properties for the non-premixed cases: the known case Sandia flame-D and the challenging case Oxy-fuel B3, where the last was operating under highly diluted conditions of CO2 and H2. However, the oxy-fuel cases A1 and A3 experimentally achieved under different Reynolds number and fuel chemical composition needs to be more investigated with higher stochastic field number. Nonetheless, premixed and partially premixed cases need to be studied applying the proposed novel approach in order to detect its capability in reproducing main combustion features which can be left for future works.